Table of Contents
Feeling worried about your car and money when your check engine light comes on and a diagnostic scan shows the p0420 code is quite natural. This is the most common complaint that the drivers have, which is also the most confusing for them. By simply understanding the reasons for this code can really help to save you time, money, and avoid unnecessary parts changes. The P0420 code tells that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) of your vehicle has noticed that the efficiency of the catalyst system has been below the minimum threshold for Bank 1.
However, the indirect cause of the problem may be the various components of the engine that are working together, although it is pointed out that The catalytic converter (CAT) is often blamed for this issue, but understanding how it works—outlined in this catalytic converter guide can prevent unnecessary replacements. We offer you a complete guide that will give you the information about the p0420 error code, the causes behind it, the proper diagnostic strategies, and the repair solutions.
What Does the P0420 Code Mean?
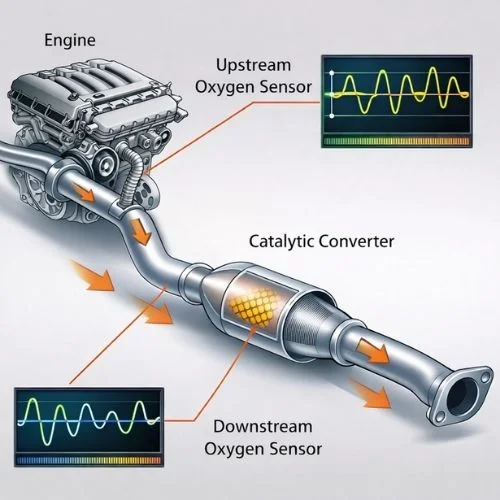
The P0420 engine code illuminates when the PCM detects after and before catalytic converter oxygen sensor readings as this enables the converter not to work efficiently. By comparing the oxygen levels in the exhaust stream you can calculate your CAT (Catalytic Converter) performance. During the normal condition the CAT allows to reduces the harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and unburned fuel by converting them into less harmful gases like nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water through oxidation.
This process creates a noticeable difference between the upstream and downstream oxygen sensor readings. When this difference is not noticeable the PCM stores the P0420 code. A related code P0430, applies to Bank 2 on V6 and V8 engines, but the underlying causes and diagnostic process remain essentially the same.
Common Causes of P0420
Before assuming your catalytic converter has failed, consider that most cats last 10 years or longer under normal operating conditions. The P0420 code can result from various issues within your vehicle’s complex emission control system:
Sensor and Electrical Issues:
- Defective oxygen sensors (upstream or downstream)
- Faulty coolant temperature sensor
- Contaminated mass airflow sensor
- Outdated PCM software
Fuel System Problems:
- Fuel injector leaks
- Wrong fuel type
- High fuel pressure
- Rich or lean fuel trims
Ignition and Engine Issues:
- Malfunctioning spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Engine misfires
- Oil consumption leading to catalytic converter contamination is a frequent cause of failure, particularly in high-mileage vehicles like those running a Nissan Altima engine.
Exhaust System Damage:
- Exhaust leaks
- Cracked exhaust manifold
- Contaminated and overheating of the catalytic converter.
- Physical damage to the cat’s internal structure.
Manufacturer-Specific Considerations
Knowing what problems are common with a specific brand can make diagnosis easier, as highlighted in this analysis of GM V8 engine issues and failures with something and help you avoid fixing things that do not need to be fixed. This is because you can look at the brand- tendencies and use that information to diagnose the problem. Understanding the brand- tendencies can really help you with this.
- Honda P0420 Issues: The Honda vehicles experiences oil consumption that contaminates the catalytic converter. Therefore, the software updates should be checked for the vintage models. The worn out spark plugs, failing ignition coils and weak downstream oxygen sensors frequently trigger this code.
- Ford P0420 Patterns: When you are trying to figure out what is wrong with the Nissan P0420 or the Ford P0420 you should check if there are any codes that have not been fixed yet. These codes might be telling you that the engine is not firing right or that there is a problem with the fuel system. If the engine is getting much fuel or if the turbo is not working properly this can cause the Ford P0420 code to appear even if the catalytic converter is working fine. Some common problems that can cause the Ford P0420 code are leaks, in the exhaust system the sensor downstream not responding enough and the fuel mixture being too rich.
- Chevrolet Characteristics: When you look at the live oxygen sensor data on a graph you can tell away if the sensors are working like they should. One issue seen frequently in Chevrolet vehicles with V8 platforms is exhaust manifold cracking, especially in trucks using engines such as the Chevy Silverado engine. If you drive your Chevrolet in the city the engine might get too much soot built up and that can trigger the code on your Chevrolet. This is something to watch out for with your Chevrolet.
- Toyota Sensitivity: Toyota vehicles are really particular about the smallest changes in how well the catalytic converter works. The oxygen sensors that are located downstream often do not work well and a lot of Toyota engines use up oil quickly which can hurt the catalytic converter. You should look for Technical Service Bulletins about how the Toyota computer system’s set up before you do a lot of repairs on your Toyota vehicle. This is especially important, for Toyota owners who want to make sure their Toyota is running well.
- Nissan P0420 Specifics: The Nissan p0420 code is particularly common in Altimas, Muranos, and Pathfinders, especially older models, where long-term engine wear may eventually require solutions such as a quality Nissan Pathfinder engine. Contaminated MAF sensors, air intake leaks, and poor heater circuit performance in downstream oxygen sensors frequently cause false readings.
Recognizing P0420 Symptoms
While the check engine light is typically the first indicator, drivers may notice several performance-related symptoms:
- Foul smell from the tailpipe
- Rough idle or engine hesitation
- Reduced engine performance and power
- Lack of acceleration response
- Decreased fuel economy
- Engine stalling
- Noticeable misfires
- Failed emissions testing
The sulfur smell indicates the catalytic converter is working overtime to reduce pollutants created by abnormal combustion conditions, which significantly reduces its lifespan.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Replacing the catalytic converter and oxygen sensors without proper diagnosis may only address symptoms rather than the root cause. Follow this systematic approach:
- Monitor Live Data: Retrieve the p0420 code along with any related DTCs and review freeze-frame data. Start the engine and monitor key parameters in real-time, paying special attention to short-term and long-term fuel trims, which reveal how the PCM and oxygen sensors interact.
- Troubleshoot Fuel and Ignition Systems: Inspect spark plugs and ignition coils for wear or damage. Check fuel injectors for leaks and verify fuel pressure is within specifications. Confirm the correct fuel type is being used and that the fuel system operates properly.
- Test Oxygen Sensors: Induce lean and rich conditions to verify both oxygen sensors respond appropriately. Introducing propane into the air intake creates rich conditions, while disconnecting a vacuum hose causes lean conditions. Both sensors should adjust accordingly with PCM parameters.
- Inspect for Leaks: Examine intake and exhaust manifolds for cracks or damage. Clean the MAF sensor to ensure accurate airflow readings. Use a smoke machine if necessary to detect exhaust leaks that might affect sensor readings.
- Verify Catalytic Converter Functionality: Use a back-pressure gauge to check for clogs within the cat’s core. Measure temperatures at the entrance and exit of the catalytic converter housing exit temperatures should be higher than entrance temperatures, indicating proper catalyst reaction.
- Update Vehicle Software: Ensure your vehicle’s PCM software is currently updated. Many manufacturers releases updates that my recalibrate emission control parameter’s, this may resolve the code without hardware replacement.
Common Repair Solutions
Depending on diagnosis results, repairs for the po420 engine code may include:
| Component | Repair Action |
| Oxygen Sensors | Replace faulty upstream or downstream sensors |
| Spark Plugs | Replace worn or fouled plugs |
| Ignition Coils | Replace weak or failing coils |
| Fuel Injectors | Repair leaks or replace defective injectors |
| MAF Sensor | Clean or replace if contaminated |
| Exhaust Manifold | Repair cracks or replace if damaged |
| Exhaust Pipes | Repair leaks or replace damaged sections |
| Thermostat | Replace if stuck open or closed |
| Catalytic Converter | Replace only after ruling out other causes |
| PCM Software | Update to latest manufacturer version |
When catalytic converter replacement is necessary, use direct OEM replacements to ensure performance matches PCM expectations.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing p0420 codes begins with consistent vehicle maintenance:
- Use high-quality fuel from reputable stations
- Perform regular oil changes using manufacturer-recommended specifications
- Replace spark plugs and ignition components at recommended intervals
- Address check engine lights promptly to prevent cascade failures
- Schedule annual inspections to catch potential issues early
- Avoid short trips that prevent the catalytic converter from reaching optimal operating temperature
- Address oil consumption issues immediately to prevent cat contamination
For more in-depth insights on engine reliability, common engine problems, and replacement decisions, explore our complete collection of engine guides.
Conclusion
The P0420 code does not always mean bad news, for your vehicle. This code is something you should know about. When you know what the P0420 code really means you can fix the problem without spending a lot of money on repairs that you do not need. If you have a Nissan P0420 code or some other kind of P0420 code, you should start by checking some things that are related to the P0420 code. These things include the oxygen sensors and the exhaust system to see if there are any leaks. You should also check how well your engine is working.
Do this before you think that the catalytic converter is broken. The P0420 code highlights that something in your car system isn’t working as expected. The catalytic converter may last for long if your car is properly maintained and is properly taken care of. In many cases the catalytic converter may last for more than 10 years or more, so replacing one without proper diagnosis can lead to issues recurring and expensive maintenance charges. Consulting to professionals and skilled mechanic may save you time and wallet too.
Frequently Asked Question
-
Can I drive with a P0420 code?
While you can technically drive with this code, it’s not recommended for extended periods. Continuing to operate your vehicle may worsen the underlying issue, potentially causing more expensive damage to the engine and emission system components.
-
Does P0420 always mean I need a new catalytic converter?
No.The catalytic converter is often the last component to replace after ruling out oxygen sensors, fuel system issues, ignition problems, and exhaust leaks. Many P0420 codes are resolved without replacing the cat.
-
How much does it cost to fix P0420?
Repair costs vary widely depending on the root cause. Simple fixes like cleaning the MAF sensor or updating software may cost under $100, while catalytic converter replacement can range from $1,000 to $2,500 or more depending on your vehicle.
-
Will P0420 clear itself?
The code may temporarily clear if the condition that triggered it resolves, but it will likely return if the underlying issue persists. Proper diagnosis and repair are necessary for permanent resolution.
-
Can a bad gas cap cause P0420?
While a bad gas cap typically triggers evaporative emission codes (P0440 series), it won’t directly cause P0420. However, fuel system issues from evaporative leaks can contribute to conditions that affect catalyst efficiency.



