Table of Contents
Contemporary vehicles have been optimized for comfort, fuel efficiency, and smoother running. In this context, there is a transmission system that has proved particularly useful in this endeavor: the CVT, or Continuously Variable Transmission. In this transmission, gear shifting is absent; in other words, there is no gear shifting. Many people are faced with this transmission type in everyday cars but are left wondering about the functioning process, reliability, and even a comparative study between this and the traditional automatic. This guide provides you with all there is to know to take well-informed decisions for yourself.
What Is CVT Transmission?
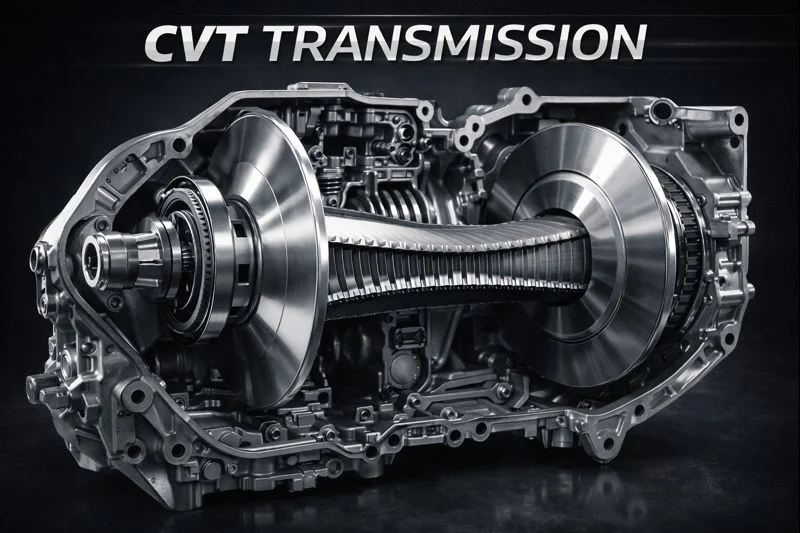
A CVT transmission is an automatic transmission system with no gears. In a shiftless transmission system, the ratio is continuous and adjustable to ensure the matching of the engine power to the road conditions. In this system, the engine operates at optimal speed with varying speeds. Since there are no shifting between gears, drivers enjoy smooth acceleration and do not experience the shock commonly associated with traditional automatic vehicles.
How CVT Transmission Works
A CVT system operates on the following principle. There are two variable pulleys, which are linked through a metal belt or chain. While one pulley is attached to the engine, the other transmits the power to the wheels. With acceleration or braking of the vehicle, the pulleys vary in size, resulting in an infinite number of gear ratios. This provides the best possible performance of the engine without any manual gear shifting.
Different Types of CVT Systems
Several designs exist, each suited for specific applications:
- Pulley-based systems commonly used in passenger cars
- Chain-driven designs for handling higher torque
- Hydrostatic systems found in industrial and utility vehicles
- Toroidal systems designed for refined power delivery
Each variation follows the same fundamental concept while offering different durability and performance levels.
Advantages of CVT Transmission
There are many reasons why automakers continue to adopt this transmission design:
- Seamless acceleration without noticeable shifts
- Improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional automatics
- Reduced engine strain and optimal power delivery
- Comfortable performance in city traffic conditions
- Compact and lightweight construction
These benefits make it especially appealing for daily commuters and fuel-conscious drivers who prioritize smooth operation and better fuel economy.
Disadvantages of CVT Transmission
Despite its advantages, this system also has some limitations:
- Higher repair or replacement costs
- Less engaging driving feel for enthusiasts
- Sensitive to poor maintenance practices
- Not ideal for high-performance or heavy towing applications
Understanding these drawbacks helps owners maintain realistic expectations and follow proper maintenance schedules.
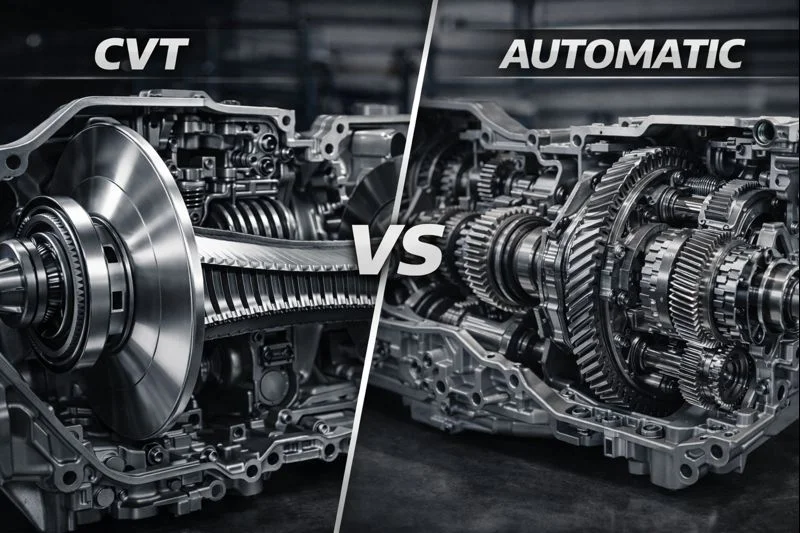
CVT Transmission vs Traditional Automatic Transmission
When comparing a shiftless transmission to a conventional automatic, the biggest difference lies in how power is delivered. Traditional automatics rely on fixed gears, while a CVT adjusts ratios continuously.
| Feature | CVT Transmission | Automatic Transmission |
| Gear Operation | Variable ratios | Fixed gears |
| Driving Feel | Smooth and linear | Noticeable shifts |
| Fuel Efficiency | Higher | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Specialized | Standard |
For drivers focused on efficiency and smoothness, the continuously variable design often offers an advantage.
Maintenance Tips for Long Life
Proper care is a must for reliability. Fluid changes with approved fluids recommended for the system, as well as timely servicing, will help prevent system overheating. Regular transmission fluid changes are essential for CVT longevity, typically every 40,000 to 60,000 kilometers.
For replacement parts and components, quality matters significantly. Consider using reliable transmission options like the Nissan Altima transmission,Honda Civic transmission, or Nissan Versa transmission for vehicles equipped with CVT systems.
Common Problems and Warning Signs
Recognizing early symptoms can prevent costly repairs:
- Delayed throttle response
- Whining or humming noises during operation
- Shuddering during acceleration
- Overheating warning indicators on dashboard
- Decline in fuel efficiency
Addressing these issues early can significantly extend transmission life and prevent complete system failure.
Importance of Quality Parts
CVT systems require components that are precision engineered. Use of low-quality components would result in increased friction, thereby accelerating the wear-down process. High-quality replacement parts help to reduce strain on the belts, pulleys, and bearings.
To better understand transmission problems, repair limitations, and replacement considerations, explore our full collection of transmission guides.
Conclusion
Understanding the working of a continuously variable transmission makes one appreciate its efficiency and smoothness. A bit finicky about its maintenance and the quality of parts used, it does deliver an amazingly comfortable and truly modern driving experience. But with proper care and dependable parts from trusted suppliers, this transmission technology can give years of plausible and exemplary service.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is CVT transmission reliable for daily use?
Yes, with proper maintenance and regular fluid changes, shiftless transmission provide reliable daily performance for commuting and city driving.
-
Does shiftless transmission improve fuel efficiency?
Yes, it keeps the engine running at its optimal speed range, resulting in better mileage performance compared to traditional automatics.
-
Is this transmission suitable for highway use?
Absolutely. Shiftless transmission excel at constant speed cruising and provide excellent highway fuel economy.
-
Are the costs of repair greater compared to automatic transmissions?
Yes, CVT repairs can be more expensive, making preventive maintenance and quality replacement parts even more important. Check our transmission options for reliable replacements.
-
How frequently should transmission fluids be changed?
Typically every 40,000 to 60,000 kilometers (25,000 to 37,000 miles), though always consult your vehicle’s owner manual for specific recommendations.